Università degli Studi di Pavia - unipv.it
Development and optimization of microfluidic assisted manufacturing process to produce PLGA nanoparticles
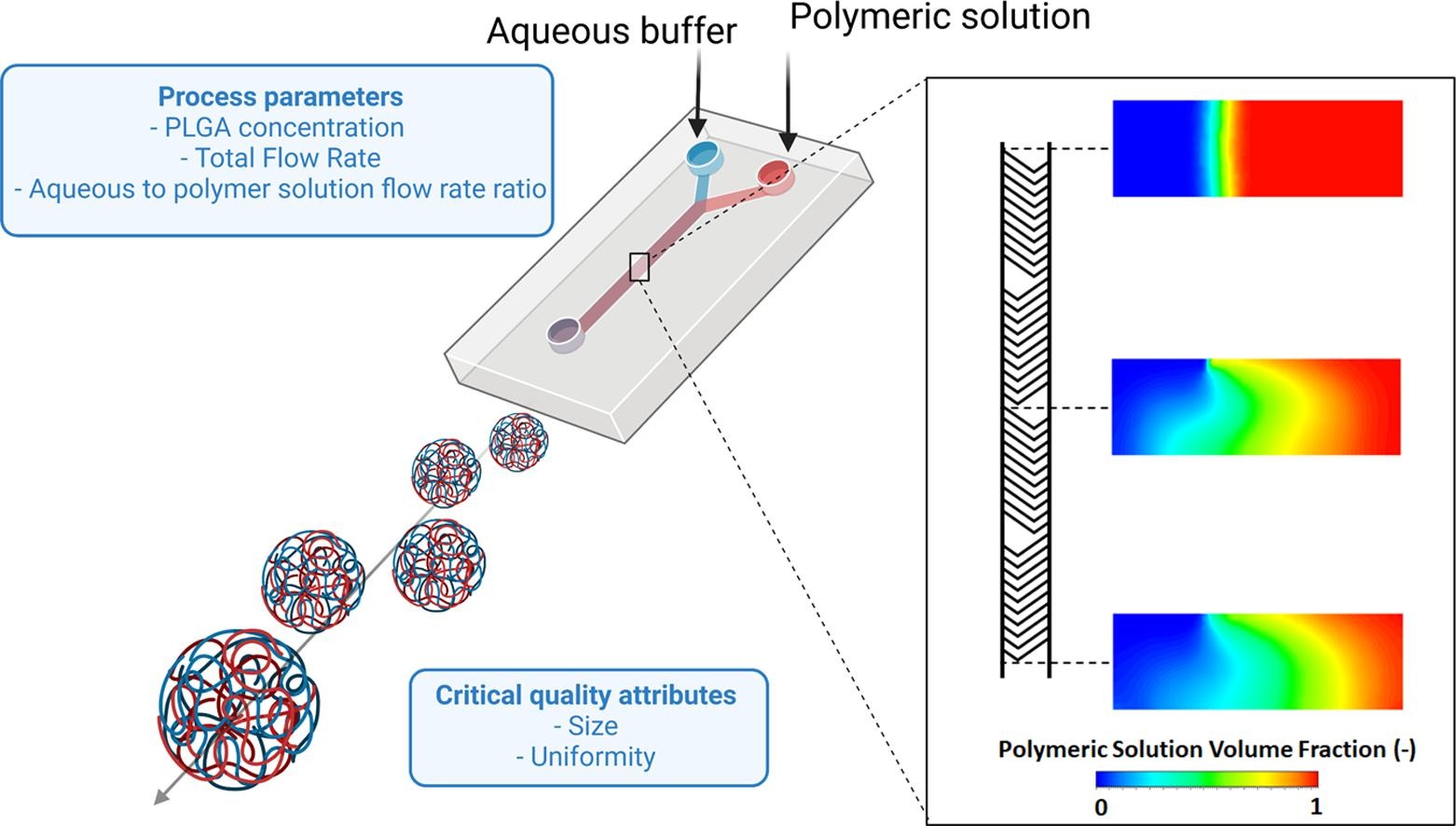
Nanomedicine consists in the application of nanotechnology in medicine to revolutionize the healthcare sector through transformative new diagnostic and therapeutic tools. In this field, nanostructures or nanocarriers (i.e., nanoparticles) are extensively used as a drug delivery system. Despite the well-defined profits offered by nanomedicines based on poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), the major barriers hampering the launch of a nanoparticles-based product on the market are batch-to-batch variations and its lack of reproducibility from the benchtop to an industrial scale production. Currently, microfluidics technology has emerged as potential tool to achieve a continuous manufacturing with a precise control over fluids mixing and particles quality attributes. This work aims at defining a tailored strategy to produce PLGA NPs, exploiting a new microfluidic device. Moreover, Design of Experiments (DoE) and computational fluid dynamics approaches were exploited to understand the main process parameters and material attributes affecting the quality of the final product as well as the NPs manufacturing process. Finally, the ability to incorporate a drug into the PLGA nanoparticles was investigated by using Curcumin as model payload reaching encapsulation efficiency in the rank 28–44%. This paper is proposed as useful guide for the preparation of PLGA NPs by microfluidic technique.